Best Cattle Feed Options for Optimal Growth and Health in Livestock
In the livestock industry, optimal cattle feed is a cornerstone of effective animal husbandry, directly influencing both growth rates and overall health. According to the National Agricultural Statistics Service (NASS), in the United States alone, over 94 million cattle are raised, contributing significantly to the agriculture economy. High-quality cattle feed not only enhances weight gain and feed conversion efficiency but also reduces the incidence of health issues among livestock, thereby maximizing profitability for producers.
Recent studies by the American Society of Animal Science indicate that the composition of cattle feed, including the balance of proteins, vitamins, and minerals, plays a crucial role in achieving desired growth metrics. Reports show that livestock on nutritionally balanced diets are more likely to meet weight gain targets within specified timeframes, fueling the industry's need for advanced feed solutions. With an ever-evolving market landscape, understanding the best cattle feed options has become paramount for producers looking to enhance livestock productivity while ensuring animal welfare. By prioritizing optimal feed formulations, cattle producers can significantly impact the growth rates, health, and overall sustainability of their herds, thereby fortifying their position in a competitive market.

Best Cattle Feed Options for Optimal Growth and Health in Livestock
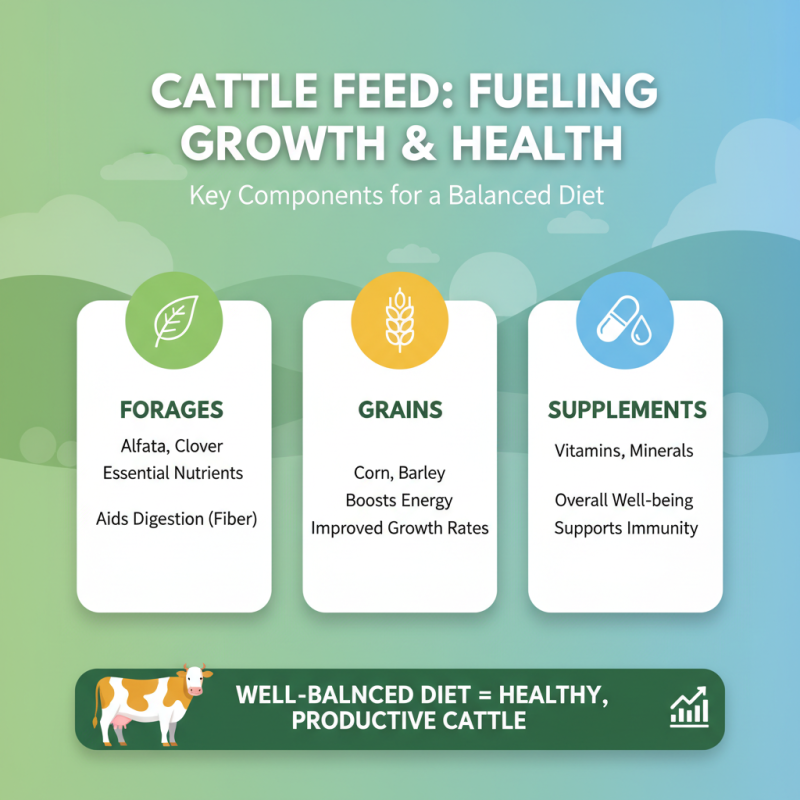
When it comes to ensuring optimal growth and health in livestock, particularly cattle, selecting the right feed is crucial. A well-balanced diet that includes a mix of forages, grains, and supplements will support not only weight gain but also overall well-being. High-quality forages such as alfalfa and clover provide essential nutrients and fiber, which aid in digestion. Additionally, incorporating grains like corn or barley can boost energy levels and improve growth rates in cattle.
Tips for Choosing Cattle Feed: Always look for feeds that are tailored to the specific age and purpose of your cattle. For example, young, growing calves have different nutritional needs compared to lactating cows or beef cattle. Consulting with a livestock nutritionist can help you craft a balanced feeding strategy that meets the unique requirements of your herd.
Another essential aspect to consider is the inclusion of mineral and vitamin supplements in your cattle's diet. These supplements can support immune function, reproductive health, and bone strength. Make sure to regularly assess the mineral content in your cattle's diet to prevent deficiencies and health issues that can arise in the long term. Investing time in developing a comprehensive feeding plan will lead to healthier cattle and enhance production efficiency.
Understanding Nutritional Requirements for Cattle Growth and Health
Understanding the nutritional requirements for cattle growth and health is crucial for optimal livestock management. Cattle are ruminants, requiring a balanced diet that includes carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. According to the National Research Council's 2021 report, a growing calf needs around 15% crude protein in its diet to support maximum daily weight gain, which can reach up to 2.5 pounds per day under ideal conditions. Additionally, energy density is essential; the total digestible nutrients (TDN) should ideally exceed 60% in their diet, ensuring sufficient energy for both growth and maintenance.
Minerals also play a vital role in cattle nutrition. A study published in the Journal of Animal Science highlights that deficiencies in essential minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and magnesium can lead to health issues such as milk fever in lactating cows and reduced growth rates in young stock. For example, adequate levels of calcium are necessary to support skeletal development and reproductive health. Furthermore, adding trace minerals such as zinc, copper, and selenium can enhance immune function and overall productivity. Regularly assessing the nutritional components of cattle feed and adjusting based on these findings can lead to healthier, more productive livestock, ultimately benefiting farm profitability.
Comparative Analysis of Grain-Based vs. Forage-Based Cattle Feed
The choice between grain-based and forage-based cattle feed is critical for optimizing the growth and health of livestock. Grain-based feeds, often rich in energy, can lead to rapid weight gain and improved feed efficiency. According to data from the National Cattlemen's Beef Association, cattle receiving a grain diet can achieve an average daily gain (ADG) of 3 to 4 pounds, significantly higher than those fed primarily on forage. The higher energy density of grains, coupled with the right supplementation, allows for quicker turnover rates, meeting market demands more efficiently.
On the other hand, forage-based feeding systems play a crucial role in promoting overall herd health and sustainability. Forage feeds, rich in fiber, support a healthy rumen environment, which is essential for nutrient absorption. Research published in the Journal of Animal Science indicates that cattle fed a forage diet exhibit improved digestive health and lower incidences of metabolic disorders. Furthermore, forage-based systems tend to produce beef with a more favorable fatty acid profile, which is increasingly valued in the marketplace due to consumer preferences for healthier meat options.
Ultimately, the decision between grain and forage must consider the specific goals of the operation, the nutritional needs of the cattle, and the long-term implications for herd health and meat quality. Balancing these factors can lead to optimal performance and contribute to the sustainability of cattle production systems.
Best Cattle Feed Options for Optimal Growth and Health in Livestock
This chart compares the average daily weight gain of cattle fed with grain-based versus forage-based feeds. Grain-based feed typically results in higher weight gain, which can be beneficial for livestock growth and market readiness.
The Role of Protein Sources in Improving Cattle Weight Gain
Protein plays a crucial role in the growth and health of cattle, significantly impacting their weight gain and overall productivity. Research indicates that cattle require a diet with a protein content ranging from 12% to 16% for optimal growth, depending on their age and stage of production. High-quality protein sources, such as soybean meal, alfalfa, and commercial protein supplements, can enhance muscle development and improve feed efficiency. According to the National Cattlemen's Beef Association, a well-balanced protein diet can increase daily weight gains by as much as 30%, illustrating the importance of adequate protein in cattle nutrition.
Tips: To ensure your cattle are receiving sufficient protein, consider conducting regular feed analysis and making necessary adjustments based on their dietary needs. Incorporating high-protein forages or supplements can bridge gaps in protein intake, particularly during critical growth phases or when pasture quality is low.
Furthermore, the availability of rapidly digestible protein sources can also affect cattle's health. Research shows that the right protein sources can improve immune function and reduce the incidence of metabolic disorders. By providing protein that is easily metabolized, cattle are more likely to achieve their genetic weight gain potential. Therefore, it is essential to monitor the protein sources in your cattle's diet and adapt them according to seasonal changes and health status.
Tips: Always consult with a livestock nutritionist to customize a feeding plan that maximizes protein absorption and supports the specific growth objectives for your herd.
Best Cattle Feed Options for Optimal Growth and Health in Livestock - The Role of Protein Sources in Improving Cattle Weight Gain
| Feed Type | Protein Source | Crude Protein (%) | Weight Gain (lbs/day) | Cost per Ton ($) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alfalfa Hay | Legume | 17 | 2.5 | 200 |
| Corn Gluten Meal | Cereal Byproduct | 60 | 3.0 | 300 |
| Soybean Meal | Oilseed | 44 | 2.0 | 400 |
| Beet Pulp | Plant Byproduct | 10 | 1.5 | 150 |
| Fish Meal | Animal Byproduct | 60 | 3.5 | 600 |
Essential Vitamins and Minerals for Optimal Cattle Development
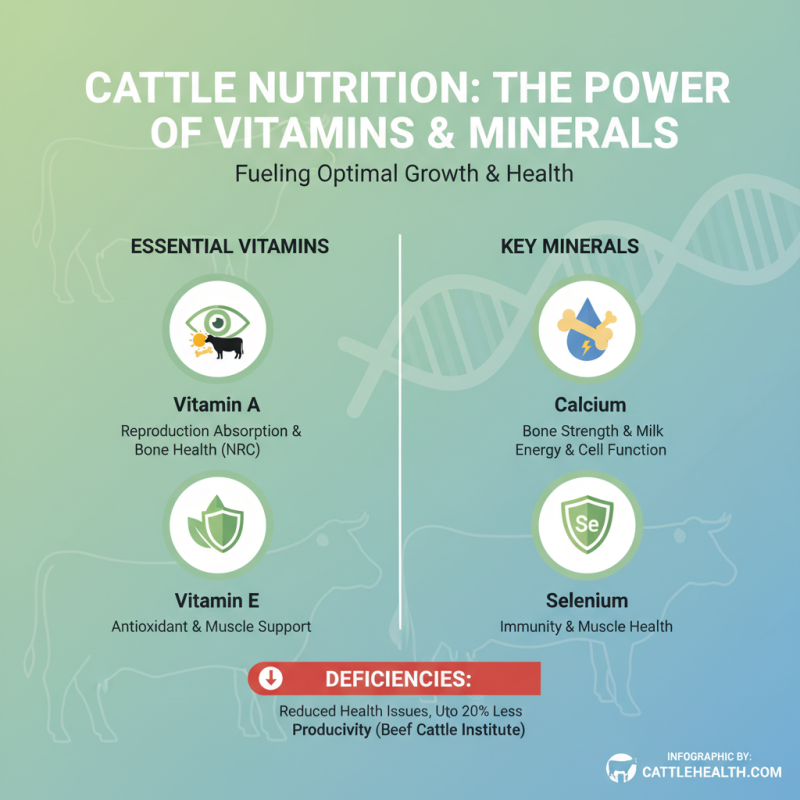
Vitamins and minerals play a crucial role in the optimal growth and health of cattle. Essential nutrients like vitamins A, D, and E, as well as minerals such as calcium, phosphorus, and selenium, are vital for various physiological processes. According to the National Research Council (NRC), adequate vitamin A is essential for reproduction and maintaining a strong immune system, while vitamin D is important for calcium absorption and bone health. A report from the Beef Cattle Institute highlights that deficiencies in these nutrients can lead to significant health issues, reducing overall herd productivity by up to 20%.
To ensure that cattle receive the proper dietary balance, incorporating mineral supplements can be beneficial. For instance, a mixture of macro and trace minerals can promote better growth rates and improve feed efficiency. Research indicates that cattle receiving balanced mineral supplementation gain approximately 0.5 pounds more per day compared to those on unsupplemented diets. This may lead to more favorable production economics, ultimately benefiting livestock producers.
Tips: Regularly monitor and analyze your cattle's nutrient intake through forage testing. Additionally, consider forming a partnership with a livestock nutritionist to develop a targeted feeding strategy that meets the specific needs of your herd. Ensuring a well-rounded diet that includes essential vitamins and minerals will contribute to the enhanced health and productivity of your livestock.
Conclusion
The article "Best Cattle Feed Options for Optimal Growth and Health in Livestock" explores the critical factors influencing cattle nutrition and health. It begins by outlining the essential nutritional requirements necessary for the growth and well-being of cattle. A comparative analysis highlights the differences between grain-based and forage-based cattle feed, examining their respective benefits and drawbacks.
The role of protein sources is emphasized as a vital component in promoting weight gain, while the importance of essential vitamins and minerals is discussed in relation to fostering optimal cattle development. Additionally, the article assesses various feed additives designed to enhance the nutritional value of cattle feed, ultimately providing comprehensive insights for livestock producers aiming to improve cattle growth and health effectively.
Related Posts
-

Top 10 Best Cattle Feed Options for Optimal Livestock Nutrition
-

How to Create a Successful Company Feed for Engaging Your Audience
-

2025 Top 5 Livestock Feed Innovations That Will Transform Farming
-

Top 5 Benefits of Using Production Feed for Your Business Growth
-

10 Essential Tips for Buying Bulk Livestock Feed for Your Farm
-

Top 10 Best Animal Feed Options for Optimal Growth and Health
